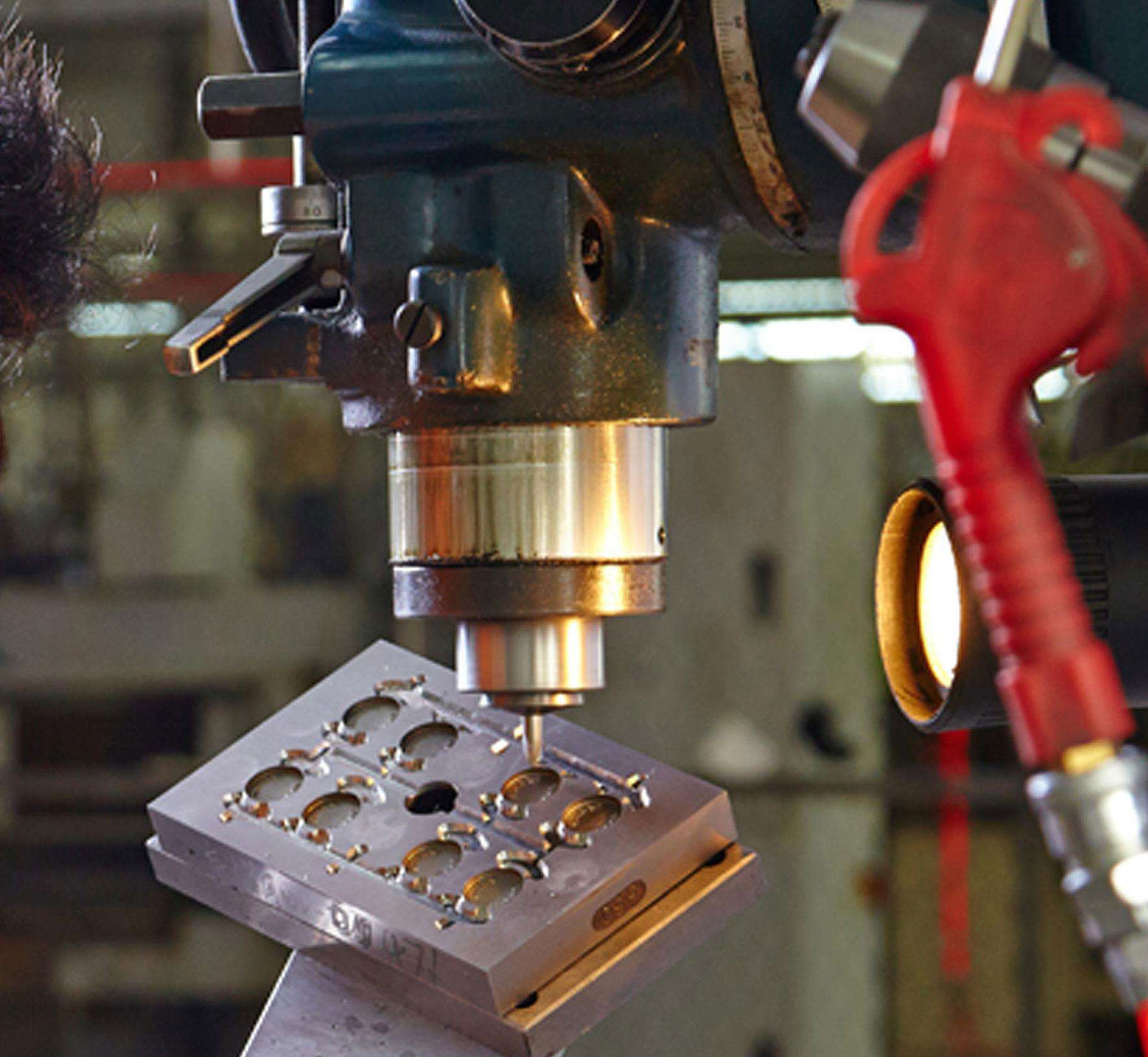
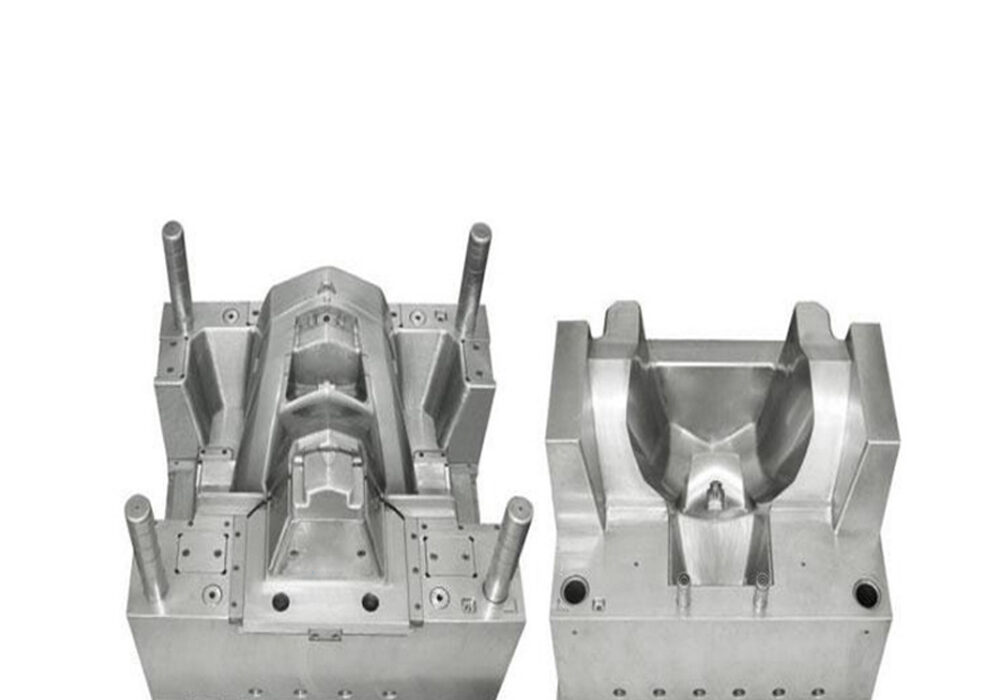
Injection molds are parts that give plastics shape and size during molding. Although the structure of the mold may vary due to the variety and performance of plastics, the shape and structure of plastic products, and the type of injection machine, the basic structure is consistent.
Injection molds are divided into thermosetting plastic molds and thermoplastic plastic molds according to molding characteristics; according to molding process, they are divided into transfer molds, blow molds, casting molds, thermoforming molds, hot compression molds (compression molds), injection molds Among them, the hot press mold can be divided into overflow type, semi-overflow type and non-overflow type by overflow method, and the injection mold can be divided into cold runner mold and hot runner mold by pouring system; Can be divided into two types: mobile and fixed. The classification of the mold is also distinguished according to the different processing techniques. The injection mold is to inject the molten plastic into the cavity of the mold with a certain speed and a certain pressure. After the plastic cools, the mold is opened to take out the molded injection product.
Compression molds are called compression molds for short. The plastic materials are directly added to the open mold cavity to close the mold. The plastic becomes fluid and fills the cavity under the action of heating and pressure, and then chemical crosslinking or physical cooling makes the product Hardening stereotypes.
Compression moulding is to use a heated mould to heat and shape the plastic sheet, and then open the mould, take out the formed product, put it in cold water for cooling. Compression molding is an important technical process in molding processing. It has a wide range of applications in industrial production and industrial processing and plays an important role in people’s lives. Generally, powder, granule, agglomerate, flake, or even a blank similar to the product is first placed in the cavity of the heated mold, and then the mold is closed and pressurized to form and solidify or cure, After demolding the product (see picture), this method is particularly suitable for the molding of thermosetting plastics (see thermosetting resins). Disadvantages are long production cycle, low efficiency, and poor dimensional accuracy of products.