“The mold is the mother of industry” is well-known to everyone. The importance of molds is more and more recognized by people, and mold design and mold manufacturing technology have also made great progress.
The innovation of mold processing technology, the wide application of various new mold materials, and the standardization and specialization of mold parts have forced us to adapt to the development of mold faster and more.
The speed increase requires that the design section can be completed to the post section in about 3 days: improve accuracy; in the design process, the processing methods of each part should be considered, and the cost of high-precision and low-processing processing methods should be used as much as possible.
The increase in accuracy and speed is consistent. The increase in speed inevitably requires an increase in precision, and the increase in precision inevitably leads to an increase in speed.
General definition of molds: In industrial production, metallic or non-metallic materials are used to produce parts or articles of the desired shape by pressure using various presses and special tools installed on the presses. These special tools are collectively called molds.
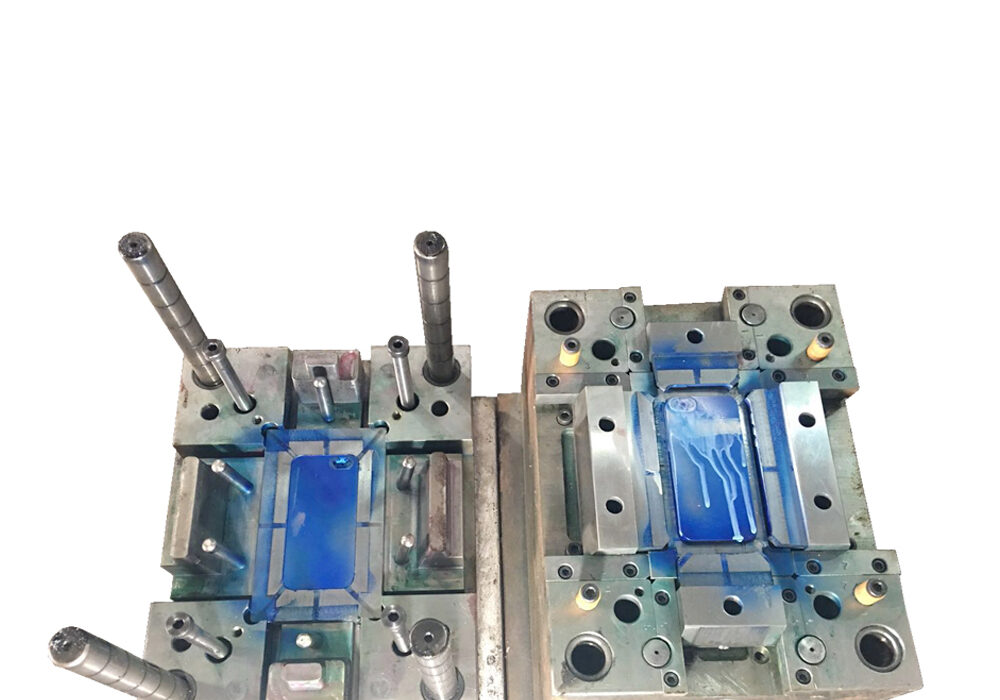
Injection process description: The mold is a tool for producing plastic products. It consists of several sets of parts with mold cavities. In the injection molding process, the mold is clamped on the injection molding machine, the molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity, cooled and formed in the mold cavity, and then the upper and lower molds are separated, and the product is ejected from the mold cavity through EJ. Check the system and finally close the mold. For the next injection, the entire injection molding process is cyclic.
Plastic mold consists of two parts: movable mold and fixed mold. The movable mold is installed on the movable template of the injection molding machine, and the fixed mold is installed on the fixed template of the injection molding machine. In injection molding, the movable mold and the fixed mold are closed to form the pouring system and the cavity. When the mold is opened, the movable mold and the fixed mold are separated to take out the plastic products.
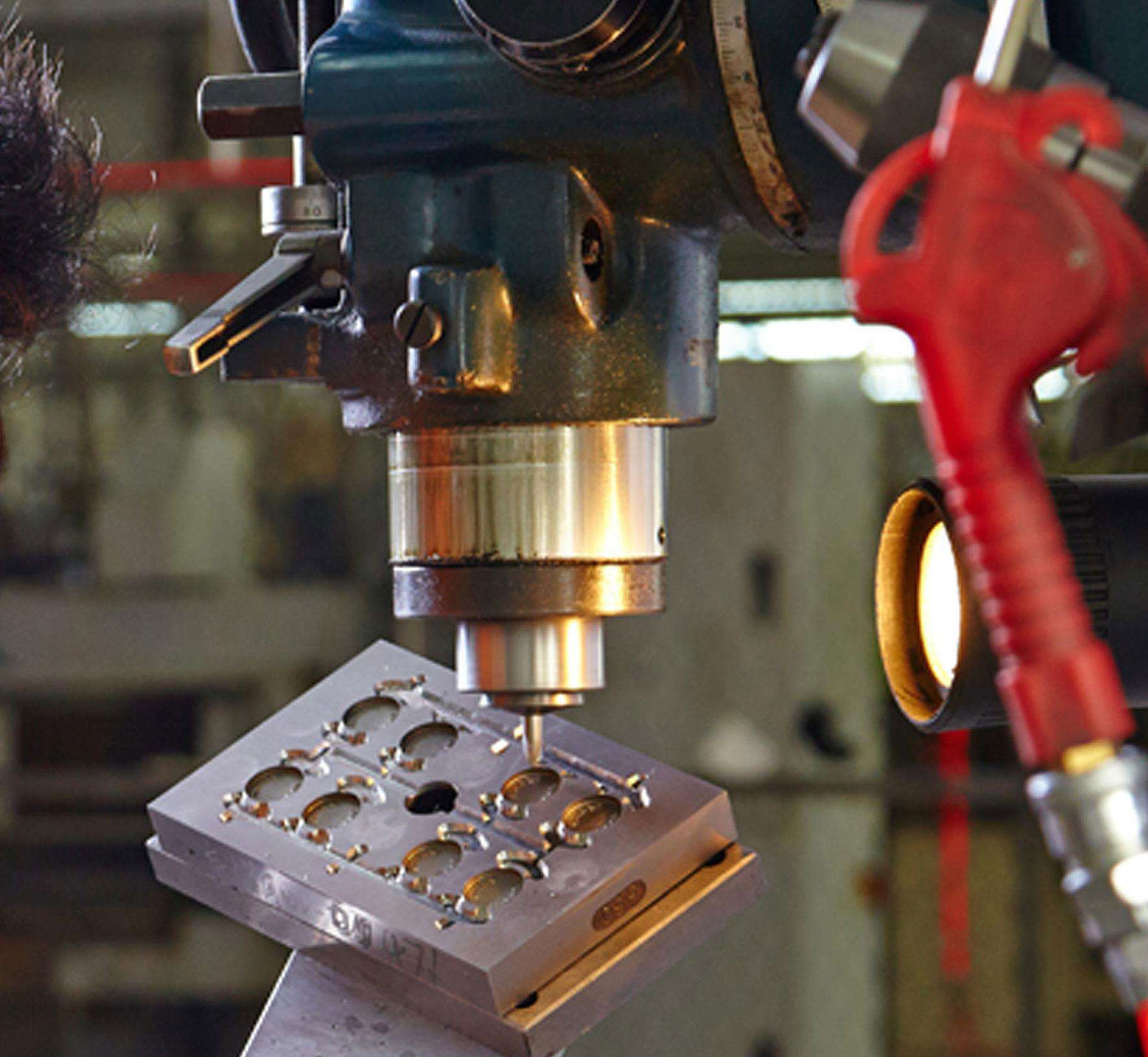
Although the structure of the mold may vary depending on the type and performance of the plastic, the shape and structure of the plastic product, and the type of injection machine, the basic structure is uniform. The mold is mainly composed of a pouring system, a temperature control system, molded parts and structural parts. The pouring system and the molded parts are in direct contact with the plastic and vary with the plastic and the product. It is the most complicated and changing part of the mold, requiring the highest smoothness and precision.
In order to remove the product from the mold, the mold must be divided into a male mold and a female mold. This interface is called the parting surface. It has the function of mold split and exhaust, but due to the difference in mold precision and molding process, it is easy to produce burrs and nodules, affecting the appearance and accuracy of the product. When selecting the parting surface, pay attention to:
- Can not affect the appearance of the product in a conspicuous position.
- When opening the mold, place the product on the side with the demoulding mechanism.
- Located in mold processing and product post-processing is easy.
- For products with high coaxiality requirements, try to design the cavity on the same side.
- Avoid long core pulling. If the core pulling mechanism must be located on the male side as much as possible, consider placing it in the mold opening direction.
- Generally, arc parts are not used, which will affect the appearance of the product.
- For plastics with good fluidity and good overflow, plug-in methods should be used to prevent burrs.
- For products with high height and small demolding volume, the middle parting mold can be used, and both sides of the parting cavity are convenient for demolding.