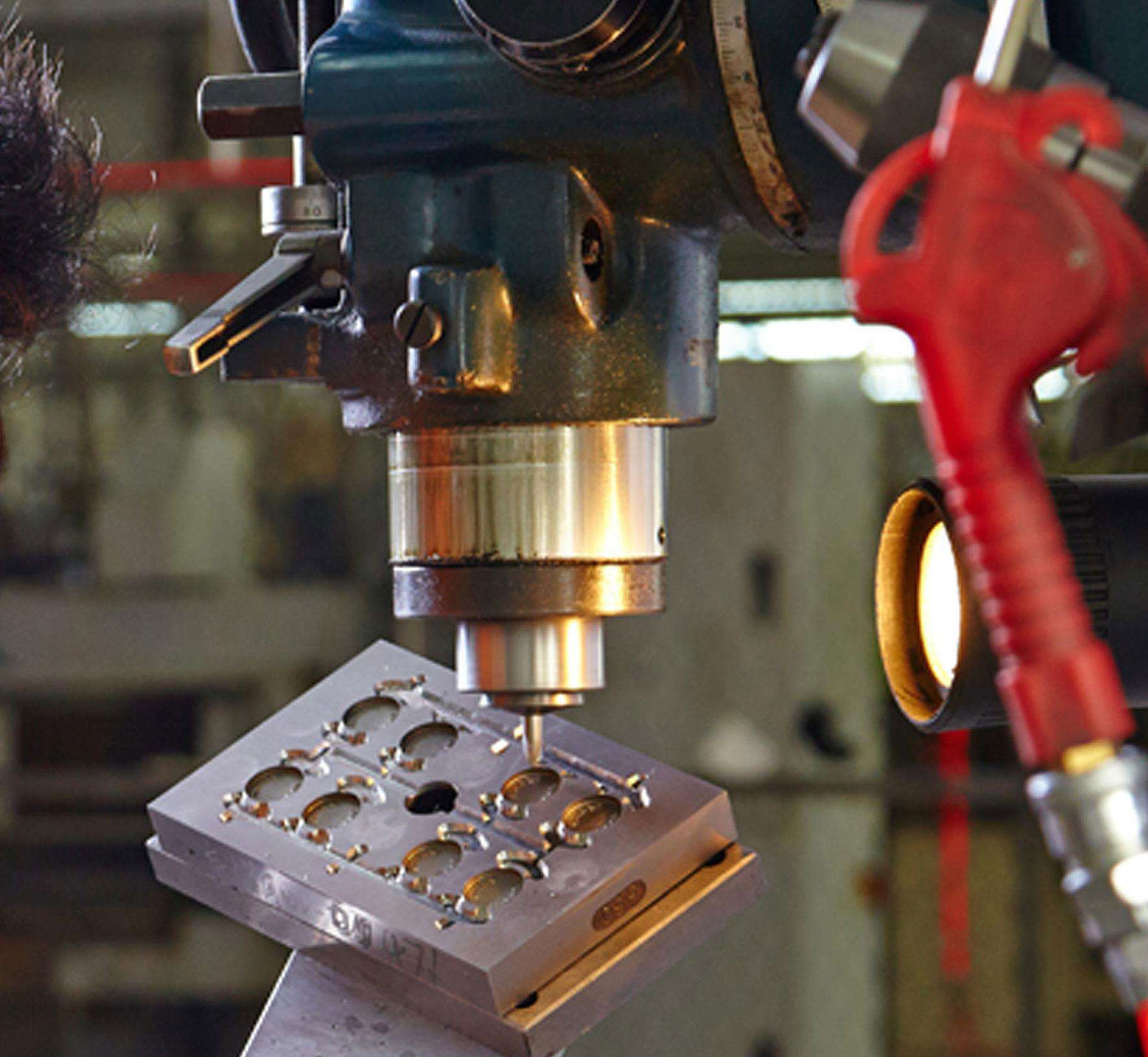
It refers to various parts that constitute the mold structure, including: various parts such as guide, demolding, core pulling and parting. Such as front and rear splint, front and back buckle template, pressure plate, pressure column, guide column, demolding plate, demolding rod and return rod, etc.
1. Guide parts
In order to ensure that the moving mold and the fixed mold can be accurately aligned when the mold is closed, a guide part must be provided in the mold. In the injection mold, four sets of guide columns and guide sleeves are usually used to form the guide part. Sometimes, the inner and outer cone surfaces that coincide with each other on the moving mold and the fixed mold are needed to assist positioning.
2. Launch organization
During the mold opening process, a pushing mechanism is needed to push or pull out the plastic products and the condensate in the flow channel. Push out the fixed plate and push plate to clamp the push rod. A reset lever is generally fixed in the push rod, and the reset lever resets the push plate when the movable and fixed molds are closed.
3. Side core pulling mechanism
Some plastic products with undercuts or side holes must be side-separated before being pushed out. The side cores can be smoothly demolded after the side cores are drawn out. In this case, a side core-pulling mechanism needs to be provided in the mold.
exhaust vent
It is a kind of groove-shaped gas outlet opened in the mold to discharge the original and the gas brought by the molten material. When the molten material is injected into the cavity, the air originally in the cavity and the gas brought by the melt must be discharged to the outside of the mold through the exhaust port at the end of the flow, otherwise the product will have air holes, poor connection, Dissatisfied with mold filling, and even the accumulated air will burn the product due to high temperature caused by compression. In general, the vent hole can be located either at the end of the melt flow in the cavity or on the parting surface of the mold. The latter is a shallow groove with a depth of 0.03-0. 2mm and a width of 1.5-6mm. During injection, there will not be a lot of molten material leaking from the vent hole, because the molten material will cool and solidify at this place and block the channel. The opening of the exhaust port must not face the operator to prevent accidental injection of molten material and injury. In addition, the matching gap between the ejector rod and the ejector hole, the matching gap between the top block and the stripper plate and the core can also be used for exhaust.
Structural parts and exhaust port of injection mold
the authorPlastic Mold
All posts byPlastic Mold
You Might Also Like
The advantages and disadvantages of 3D printing prototype spray paint and UV highlight treatment
Plastic Mold2021年9月26日
In the process of making 3D printing models, some products with high appearance requirements often need to be spray painted...
Factors affecting the price of beryllium copper
Plastic Mold2021年7月28日
International economic situation. The correlation between the commodity market and the economic situation is obvious, especially as the world economy...
How to determine the thickness of aluminum alloy die castings
Plastic Mold2021年7月22日
In the design process of aluminum alloy die castings, many customers are uncertain about the thickness of aluminum alloy die...
Precision CNC machining manufacturers explain how CNC CNC lathes are processed
Plastic Mold2021年7月22日
According to the introduction of precision CNC machining manufacturers, the large-scale CNC machining parts are made of bar materials, and...
Talking about the Application of Beryllium Copper in Plastic Mould
Plastic Mold2021年6月28日
Talking about the Application of Beryllium Copper in Plastic Mould Nowadays, more and more beryllium copper mold materials have...